


The menus themselves are highly application-oriented and thus come with a set of predefined settings depending on the purchased license, but can also be configured freely. Both, the import of the predefined menu settings as well as the customisation can be achieved through "Customize Ribbon" which can either be reached through "Start » Customize Ribbon" or right-clicking in the menu area and selecting "Customize Ribbon". There you can either import one of the predefined menus by clicking the import button or create a fully individual menu of your own by selecting the desired menu options in the left dropdown and drag them to the right. Please note that you have to open a "Ribbon" on the right to which you want to add a certain menu option.
It is possible to try out every menu setting regardless of your license, meaning for example you could import the settings of the Ultimate Edition possessing only the Basic Edition, when trying to use certain functions not included in your edition, however a dialog will pop up informing you. The best part is you can export your customised menu, so it will be available to you when you switch editions for example, if you tried out the demo edition and decided to purchase a license. Furthermore, each menu button itself can be further customised, you can decide the size of each button as well as if the text should be shown or not.

There is a drop down to quick change your menu.
See how to individualize new buttons for your ribbon menu:
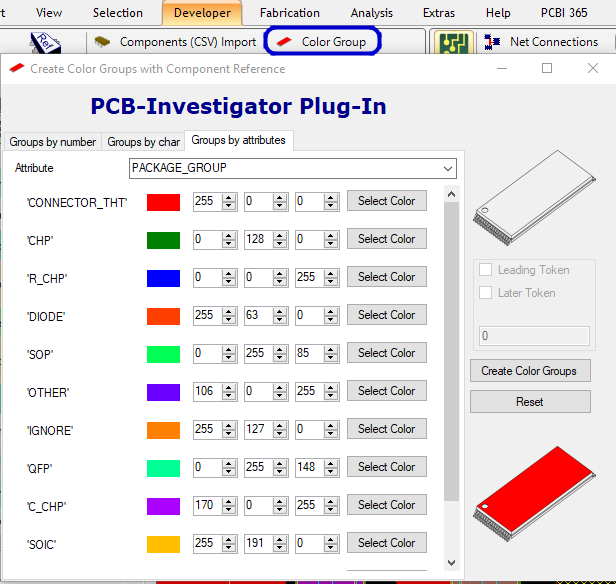
You can get to Colour Group via Developer » Color Group.
In both cases the colour scheme can of course be customised to fit your preferences.
Here is an example how it can look for package group coloring:

Sync Actions

Image Compare - Specific Settings

General
Advanced
List Compare - Specific Settings

Diff Tool Settings
External Diff Tool
Note(!): To provide the program with the list view data, two temporary csv files are created. The paths to these files are appended as arguments to the program call. Only programs which support csv files, which allow command line parameters and which do not require a special syntax to define the files to be compared (eg. like a prefix before the filepath), are supported.
Instance Snchronization - Illustration
If you want to use the synchronization functionality, the new instance of PCB-I must be opened with the button 'Open new instance'

To activate the synchronization functionality, you must click the 'Sync On/Off' button on all instances you want to synchronize.
A green label (with white text) appears in the upper left corner of the main viewport. It shows the process ID under which the PCB-I instances run. The window called MAIN is the root instance. When it is closed, all other windows are closed too and the process is terminated. All windows called CHILD can be safely closed without closing other windows. There is no influence on the synchronization functionality, whether the window is MAIN or CHILD.
Once the windows are synchronized, all functionality and actions set in the Sync/Compare Settings are synchronized between all instances.
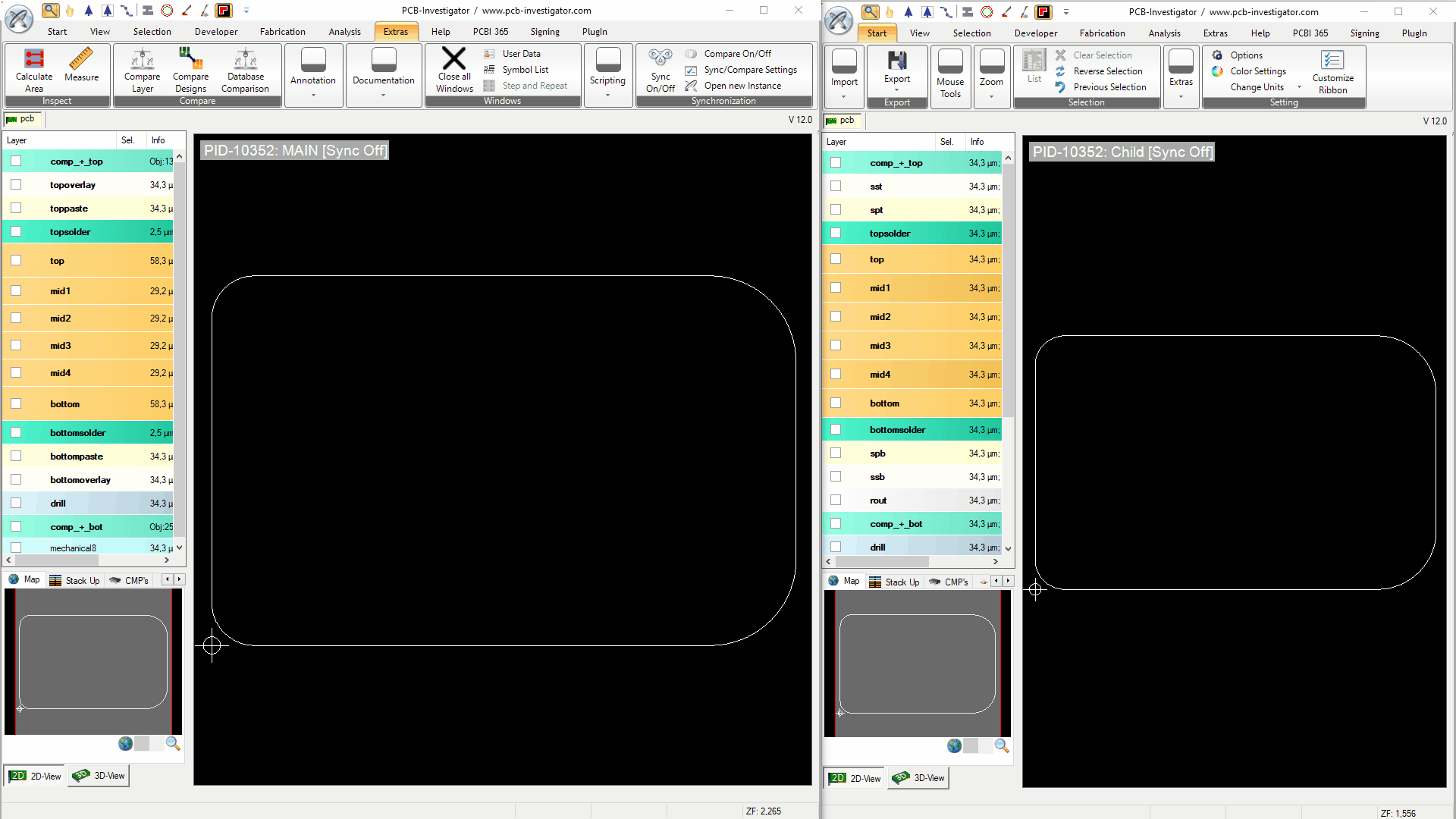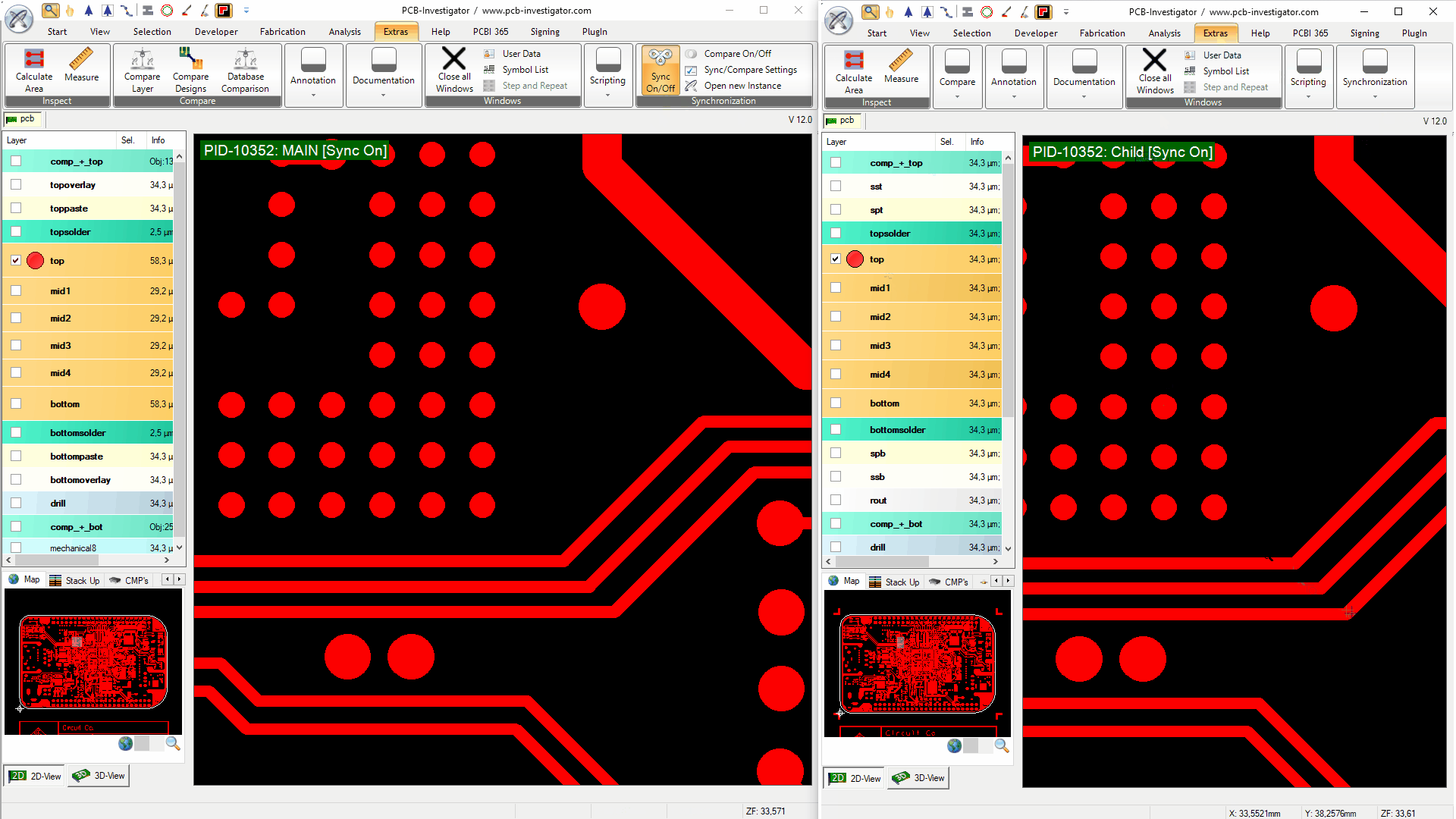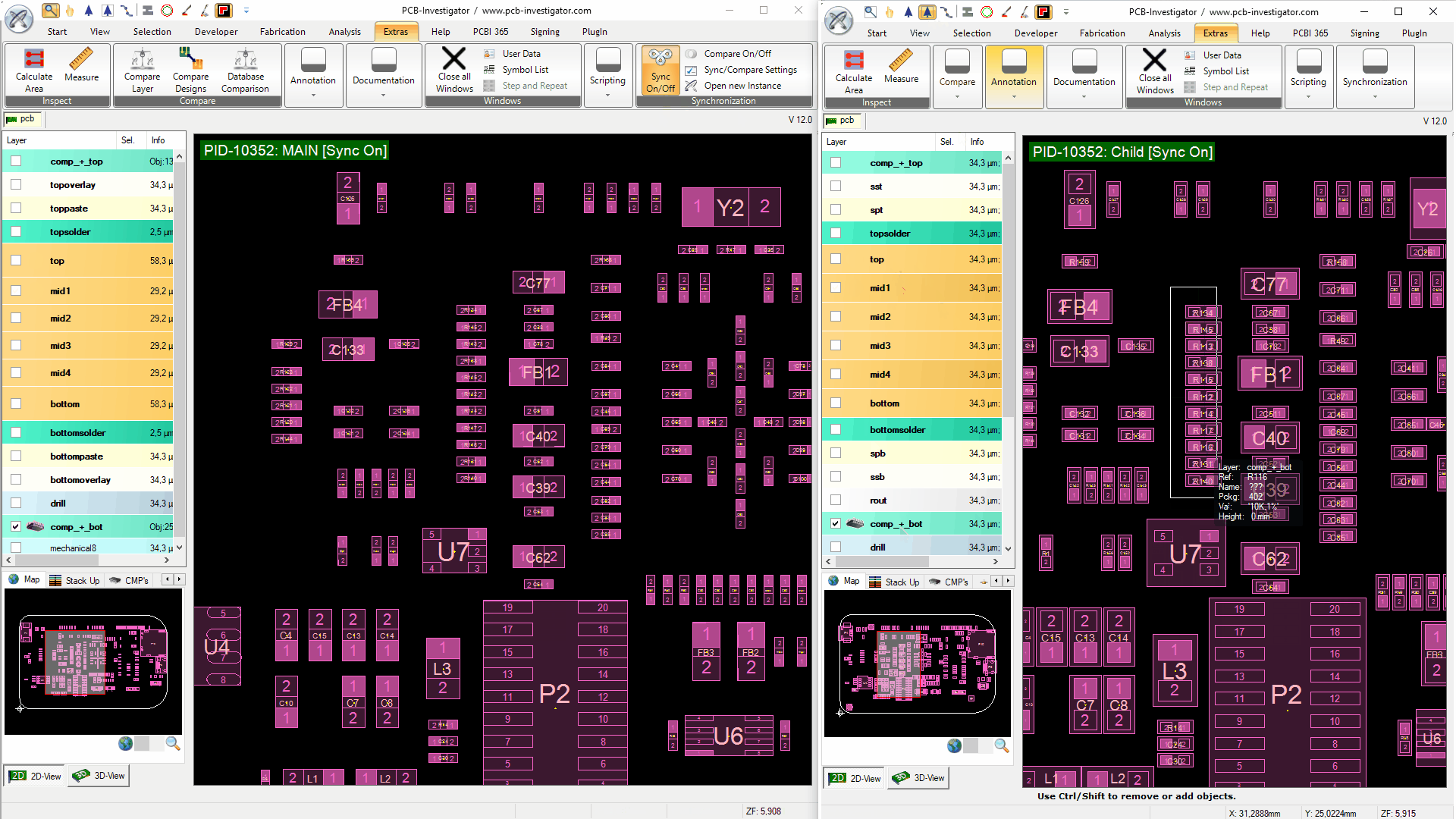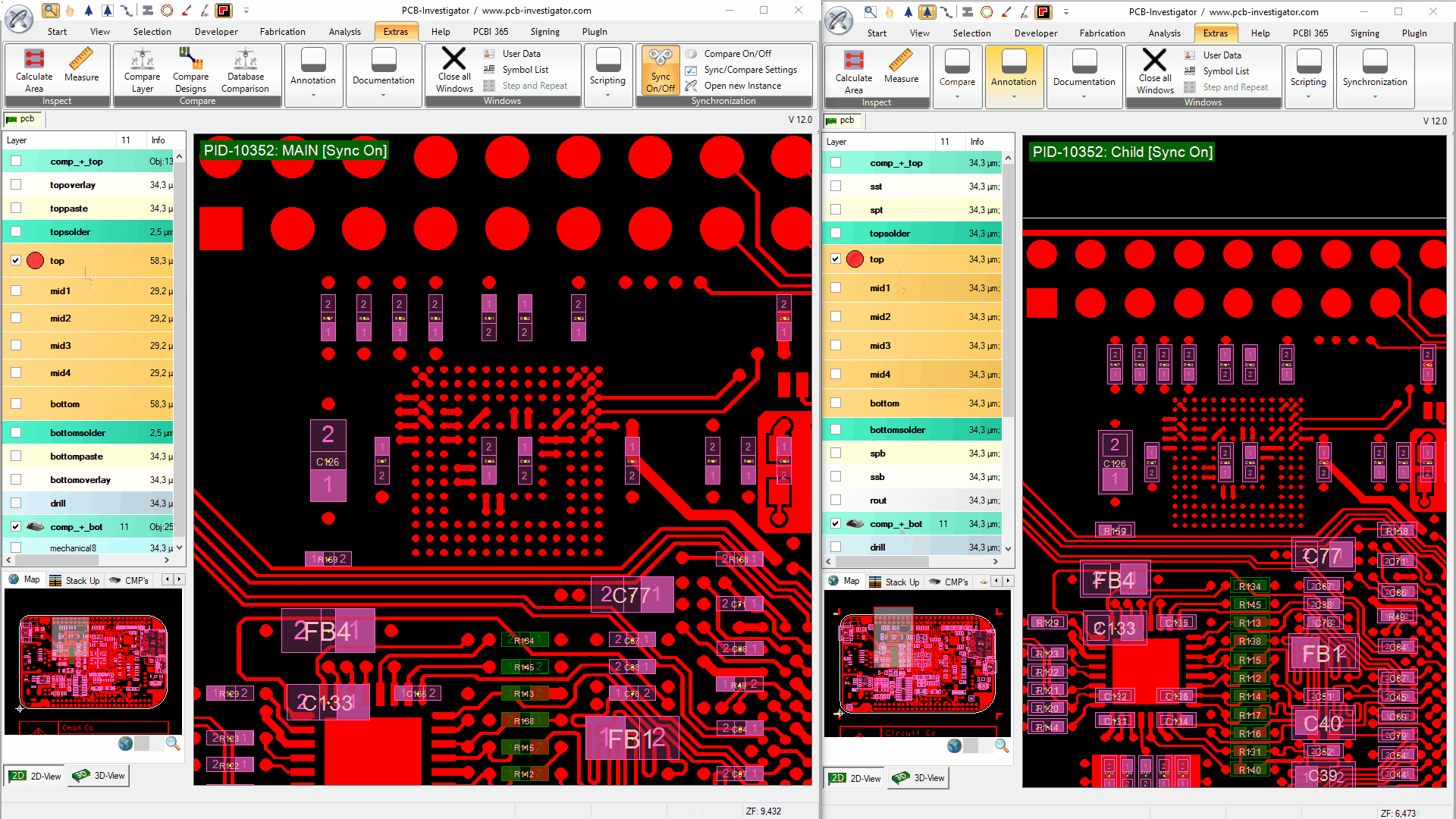
To activate the synchronization functionality, you must click the 'Compare On/Off' button on two instances you want to compare.
This also activates the live synchronization for both windows, if it was not turned on before. If the compare is active, all differences between the two opened designs are marked with white lines. The algorithm groups areas with many small changes to a larger area. The exact compare behaviour can be fine-tuned in the Sync/Compare Settings.

If the synchronization is active and any list view is opened in both instances, differences are marked in different colors (List Compare). A round button in the bottom right corner of the list shows that the compare is active. List views of which the button is showing the same number are compared. List views with compare active are also synchronized (sorting, scrolling, filter). Rows with red coloured cells are available in both lists but differ from each other. Green coloured rows and gray coloured columns are only available in one list. To identify rows that belong together, the most meaningful column for each list is used.
By clicking on the round button, a menu can be opened. There you can switch the things that should be synced on and off individually. The blue button in the menu opens an external diff tool. It uses the diff tool set in the Sync/Compare Settings. You don't need to install a separate diff tool for this. By default, one integrated in the PCBI is opened.

1) After you have adjusted the settings for the next dimensionings you want to add, you can press "Add".
Then, move to the graphic interface to choose two points on your printed circuit board you want to select for measuring their distance. PCB-Investigator thereby helps you with reference points to easily mark e.g. the edge or centre of a component. To set a marker for dimensioning use a right-click. A double-click allows you to change the location of the set marker by entering new values for x and y. You can also easily relocate the connecting line and its associated text information with holding the right mouse botton and shifting the line in its wanted position.
2) Here, you can adjust the settings for the layer, the text and the type of the new dimensioning you want to add.
3) There are three more options you can adjust before adding a new dimensioning: text size, text rotation and font.
4) You can also determine the colors that should be used for the visualization of the dimensioning: line color, text color, back color.
5) Clicking on "Apply" allows you to subsequently change the settings of (3) and (4) for all dimensionings you have determined so far at once.
6) In this list, you will find a overview of all dimensionings you have determined with all their relevant information. You can also adjust the settings by double-clicking on the intended configuration. A right-click on a dimensioning will highlight the appropriate dimensioning in the graphic interface.
7) Here, you can choose the unit you want to use for your dimensionings. Selecting "auto" will apply an automatically choosen unit (most practical solution) for each dimensioning. To avoid misunderstandings using "auto", you should indicate the unit for each of your dimensionings (2).
8) "Set Bounds Dimensionings" sets the dimensionings for your overall printed circuit board (lenght, width).
Example for dimensionings on a design:
View Dimensionings:
To display or hide your dimensionings, click on the framed symbol which can be found under "View".
With PCB-Investigator, you have the ability to obtain a realistic 3D view.
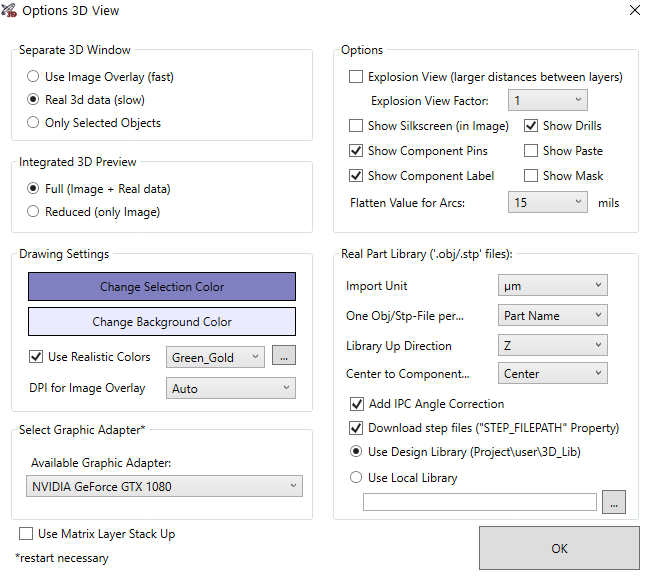
This guide explains how to create accurate 3D views and ensure their inclusion when exporting to various formats such as STEP, OBJ, and WebGL. To do so, follow these steps:
Here, you have three options to choose from:
If you wish to export your 3D design, you have the option to do so in STEP, OBJ, STL and WebGL formats.
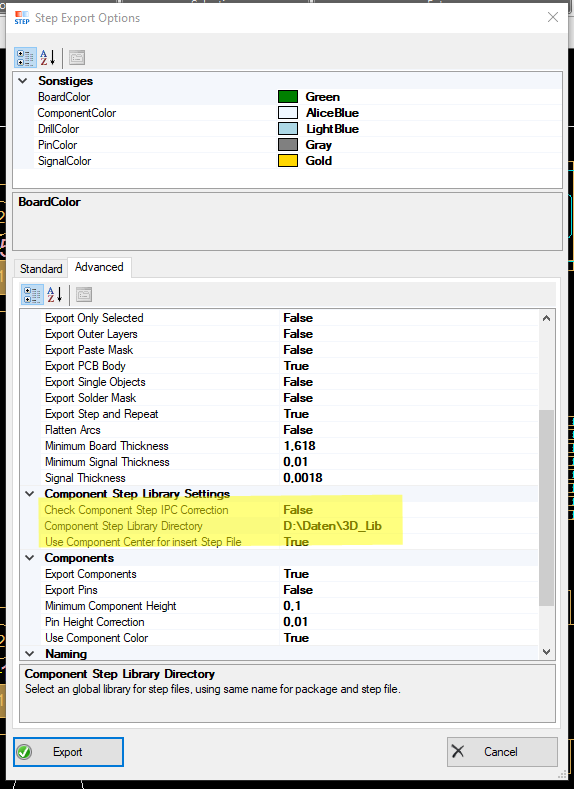
see more to step format here!
To compare testpoints on both designs, there are several settings you should consider. At the top, there is an option tab. The comparison will just check the position, the diameter and the net, any other attribute will be ignored.
After checking the important attributes, the comparison can be started. Click the "Compare Testpoints" button to start the process.
You have many options to define the testpoints:
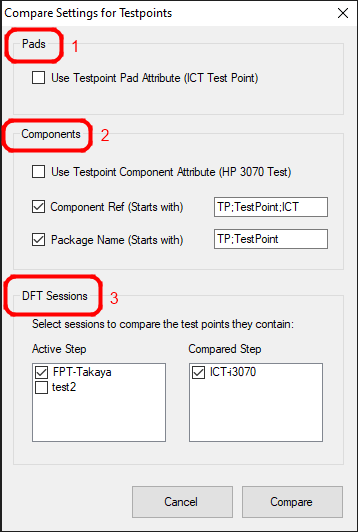
After pad attributes (1), there are different options to find component testpoints (2) and in the third block you can select existing DFT sessions (3) for testpoint definitions.
The results will be shown after the waiting dialog is shut down. Before checking the results, it is necessary to know in what state the result may be.
Possible result states are:
As you can see, this overview is also available in the dialog. It shows you the summary of all results. There is also a checkbox which can be used to list only results with a different state.
Result state definition:
The results which will be shown may look like the following picture.

The different colors show the result status. Clicking one result entry will show you the details below. For example:
Clicking the "different!" state result, the detail view may look like this.
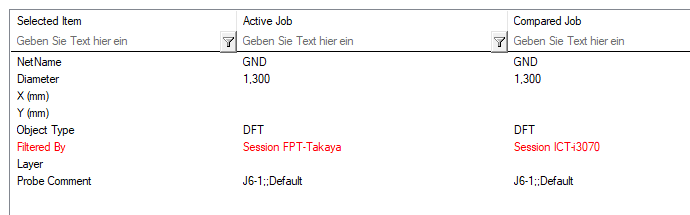
The red colored attributes show you the differences between testpoints of the designs. Black colored attributes are identical. The red and black color depends on the state of the result.
Watch our PCB-Investigator - Graphic Board Compare Video here:
Tutorial: Graphic Board Compare:
Watch our PCB-Investigator - Database Compare Video here:
Tutorial: Database Compare:
Watch our PCB-Investigator - Instance Sync Compare Videos here:
Tutorial: Instance Sync (CAD data)
Tutorial: Instance Sync (PDF document)
With the PCBI Documentation Plugin it is easy to generate images for reports or documentation.

There are many options to generate your image:
Black and white: Change colours for all layers to a greyscale image
Draw Copper Layer: Activate the top/bottom copper layer
THT/SMT/Pressfit/Other Components: Filter the technology type of the components
Fill Components: Allow to switch between filled and outline drawing for components
Draw Outline: Option to show board outline
Draw Size: Display ruler for width and height of the PCB
Draw Mask/Paste/Silk Screen Layer: Activate the layers with specific type
Draw Board Color: Option to fill the outline
Draw MPN Outline: For additional Part/Package information they are shown extra (in the overview image with Cyan)
Custom Layer
There is an option to define your own layer list/Views and Synchronize with PCB-Investigator

And the Real View option, this define fix views as realistic image for your virtual twin.

Use The Find Dialog or Search Textbox to get a overview with all found Components, nets and properties:


If you use the space key, the quick search appears and you can use some chars to filter the search results:
> search for attributes and properties on copper and other ODB objects
! search for components e.g. type the reference or a part of the reference
? search for attributes e.g. the mount type
$ serach for layer names, you can activate them or deacitvate it without scrolling in the layerlist
% serach for nets, use net name or part of them to find the relevant net and select/highlight them
Note: Quick search is available in V17 and preview beta version! This feature replace the old metro style menu and is available by pressing the space key on the keyboard.
In the search manager it is possible to define different search types, it is possible to add your own plugins with individual searches to the Search Provider List.
Default there is a web serach, a part search and a package search. In each of them it is possible to add additional serach properties to e.g. search in a different library or serach for customize properties.

The Search for... Context menu is on many places available (nearly each list view supports the serach), you can directly start e.g. a bing serach without copy the property or check for existing MPN on your favorite website.
For more information how to customize the search contact support@easylogix.de