



To change e.g. the order of layers, you have to open the "Layer Matrix" menu, which can either be directly accessed through right-clicking in the layer panel and selecting "Open Matrix" or selecting "Fabrication » Matrix" in the main menu. There you are able to i.a. add new layers, load predefined standard stack ups, and even print a report of your stack up or export it as CSV.
In addition to the order of the individual layers every other information like default stackup, layer type, hights, layer attributes, material, colour, etc. can also be adjusted to fully fit your needs. Once every configuration is in order the printed curcuit board can thoroughly be inspected by selecting one or more layers (by simply clicking on them) for visual representation. By default, each layer is assigned a specific colour so that it can quickly be identified which parts and layers are belonging together. Related colours and layers can be found between the checkbox and the layer name. Should the colours not meet your preferences, they can also be adjusted either seperately through right-clicking on the concerning layer and selecting "Set Color of Layer" or globally through "Start » Setup Colours".
For example, you can choose a standard stackup for your pcb. To do so, right-click on "File" in the upper left corner of the menu. There, you have the option to choose one of the default stackups.
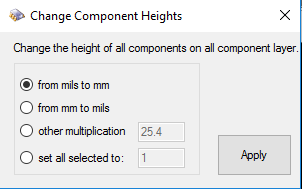
Component height is an important component property that is deeply attached to it. In earlier versions of ODB++ this property was just a number without unit. Since PCB-Investigator needs a unit for certain features like the 3D visualisation it assumes the unit "mils" by default. The Change Component Heights dialog which can be reached by Developer » Component Heights is a fail-safe that allows you to change the unit if it is falsely assumed by the program. Please note that this option only affects the component height property.
With the Filter option you can handle components only on active layers, only selected components or all components.
The NetGroup Wizard can be used to create net groups and to add or remove nets to them.
Open the NetGroup Wizard with clicking the "Net Groups" button.
The following dialog will show up.
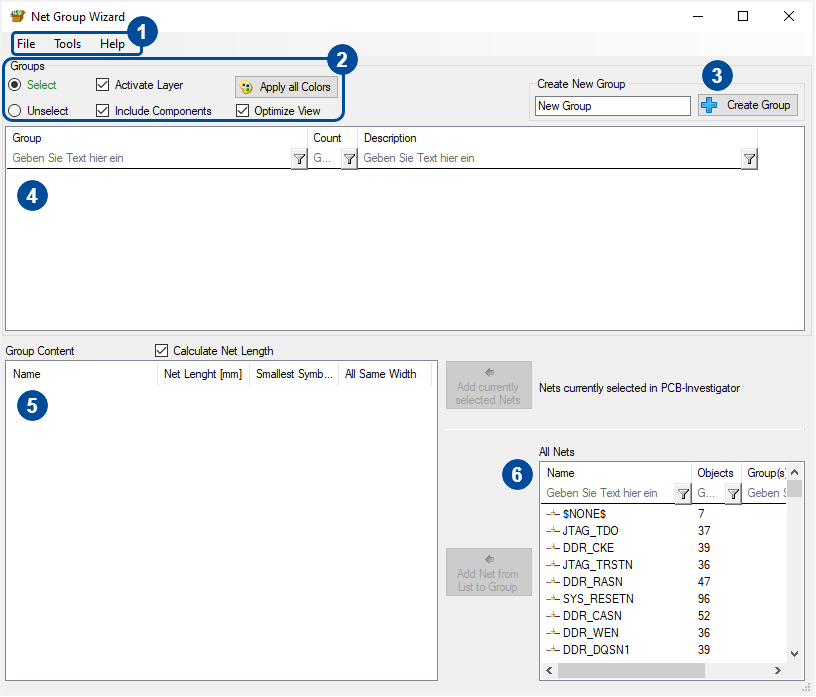
1. The two important tabs contain the following options.
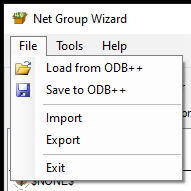
The net groups are always stored within the ODB design. Sometimes, you want to import net groups from another design. Prior to that, export the current net group to have a backup of them. In the import you can select between different file formats (xml, txt, dcf, dcfx, csv, rulf) to add net groups from other software (e.g. Xpedition or Zuken) or if you select xml from other PCB-Investigator exports.
Import Format List:
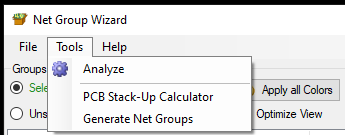
The "Tools" tab has three important functions.
To create net groups, the net names will be used. The number is the number of letters to be tapped. All nets with the same beginning will then be added to the net group. The net groups names depend on the tapped letters.
2. The summary of controls allow you the following operations:
3. The button "Create Group" allows you to create you own groups with the desired group name.
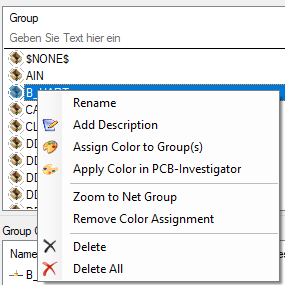
4. This control contains all net groups which are deposited in the ODB dataset. More options to edit net groups can be found by right clicking on a net group.
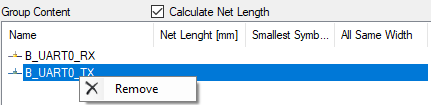
5. Every net of the net group will be shown here, if a group in the group view (4) is selected. To remove a net of the net group, right click the net you want to remove and click remove.
6. If y net group (4) is selected, you can add single nets to the net group with clicking a net in the view with the number 6 and clicking the add button. There are two different add buttons:
For more details have a look to this short video:
By clicking on the Panel Builder symbol, the following dialog will open:
1. Clicking on "Add a new Step" enables you to create an additional step.
2. "Import Step" allows you to import a new design / step from another file.
3. "Create Panel (Simple)" is described separatly and in detail under the post "Create Panel (Simple)".
4. "Create Panel (Intelligent Nesting)" is also explicitly described in an extra post.
5. "Edit Step" is an additional functionality to be used to individually place the origin.
6. The "Drag and Drop" option allows you to manually place the steps on your panel. Clicking on it, the following dialog will open:
7. Clicking on a step in the list, you can transform the selected step by rotating it or moving it in individually set intervals.
8. This list shows all steps currently placed on the relevant panel with its most important information.
9. Clicking on "Set Fiducials" allows you to define markers on your panel. The following dialog will therefore open:
10. "Add Routing" is used to define the routing for your panel. Clicking on "Add Routing" will open the following dialog:
In the File menu you find an extra dialog "cutout editor" see here
11. For defining holes on your panel, click on "Set Holes". The following dialog will be opened:
12. "Set Profile" allows you to define the profile of your panel. The following dialog will be opened when clicking on it:
13. Here, you can add another step on your current panel by choosing the step out of the provided list options. You are able to select each step that has been defined for this design.
14. Clicking on "Apply" applies all changes made by you on your currently opened design.
1) After you have adjusted the settings for the next dimensionings you want to add, you can press "Add".
Then, move to the graphic interface to choose two points on your printed circuit board you want to select for measuring their distance. PCB-Investigator thereby helps you with reference points to easily mark e.g. the edge or centre of a component. To set a marker for dimensioning use a right-click. A double-click allows you to change the location of the set marker by entering new values for x and y. You can also easily relocate the connecting line and its associated text information with holding the right mouse botton and shifting the line in its wanted position.
2) Here, you can adjust the settings for the layer, the text and the type of the new dimensioning you want to add.
3) There are three more options you can adjust before adding a new dimensioning: text size, text rotation and font.
4) You can also determine the colors that should be used for the visualization of the dimensioning: line color, text color, back color.
5) Clicking on "Apply" allows you to subsequently change the settings of (3) and (4) for all dimensionings you have determined so far at once.
6) In this list, you will find a overview of all dimensionings you have determined with all their relevant information. You can also adjust the settings by double-clicking on the intended configuration. A right-click on a dimensioning will highlight the appropriate dimensioning in the graphic interface.
7) Here, you can choose the unit you want to use for your dimensionings. Selecting "auto" will apply an automatically choosen unit (most practical solution) for each dimensioning. To avoid misunderstandings using "auto", you should indicate the unit for each of your dimensionings (2).
8) "Set Bounds Dimensionings" sets the dimensionings for your overall printed circuit board (lenght, width).
Example for dimensionings on a design:
View Dimensionings:
To display or hide your dimensionings, click on the framed symbol which can be found under "View".
Clicking on “Add” that can be found under Fabrication, the following window will open.

You have the possibility to add 5 different types of objects:
1. Line
2. Pad
3. Surface
4. Arc
5. Text.
The here mentioned objects correspond to the different types of objects ODB++ provides.
The description of the placement of lines forms the basis for the explanation of the addition of all the other objects. Overlapping configuration options will only be described here.
To edit objects, you first have to select the object you want to choose for edition (either by double-clicking or by using the selection tool). After that, by clicking on “Edit”, the following window will open showing the parameters of the currently selected object.
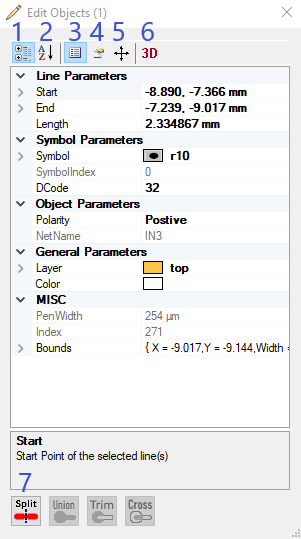
There are 4 general options of editing objects:
1. You can either sort the properties by categories or
2. according to the alphabet. It´s also possible to change the properties by entering new values.
3. You will also see all attributes belonging to the selected object. By clicking on the green plus symbol, you can add attributes. The red cross will remove the selected attribute.
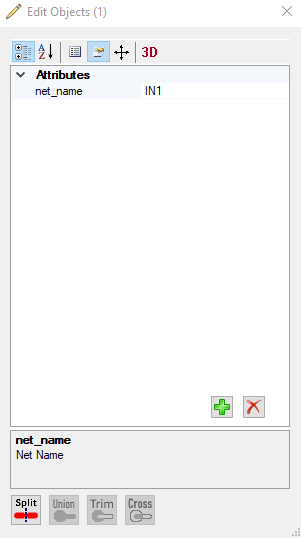
5. Editing the objects also refers to changing their position by moving, rotating or oversizing them.
Here, you have some different options to adjust the current position of the selected object. You can move (in specific steps per mm) and rotate your object (change angle) or oversize the object by entering new values for its size or a certain percentage for the augmentation.
6. It´s also possible to look up the 3D Step File Path that is deposit for the currently selected object. You can also adjust the 3D parameters by changing the values for the offset and rotation regarding X, Y and Z axis.
7. At the bottom part of the dialog, you can see 4 further options for editing objects (only the applicable ones will be shown in colour):
Symbols / Objects are stored in the symbol library. You can either access it when e.g. adding or editing objects or you can directly open the symbol library.
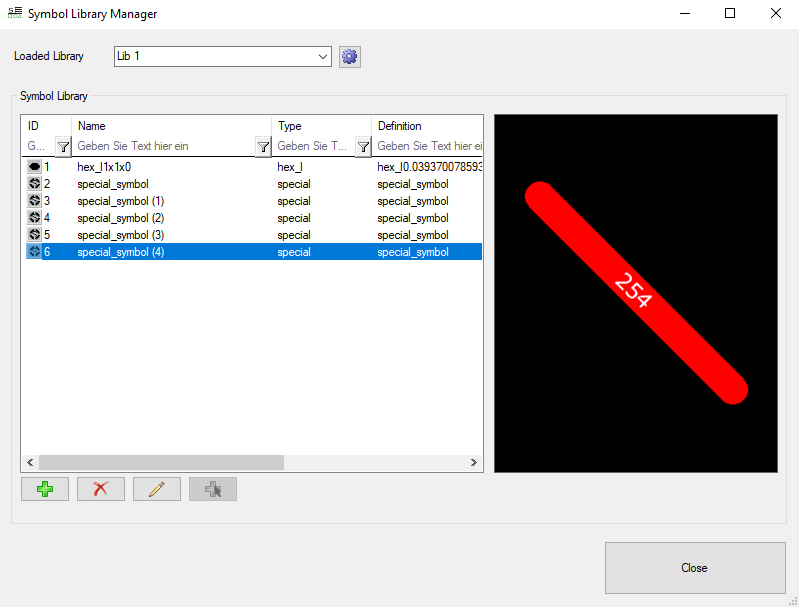
By clicking on the tab “Symbol Library” which can be found under the ribbon “Fabrication”, the following window will open.
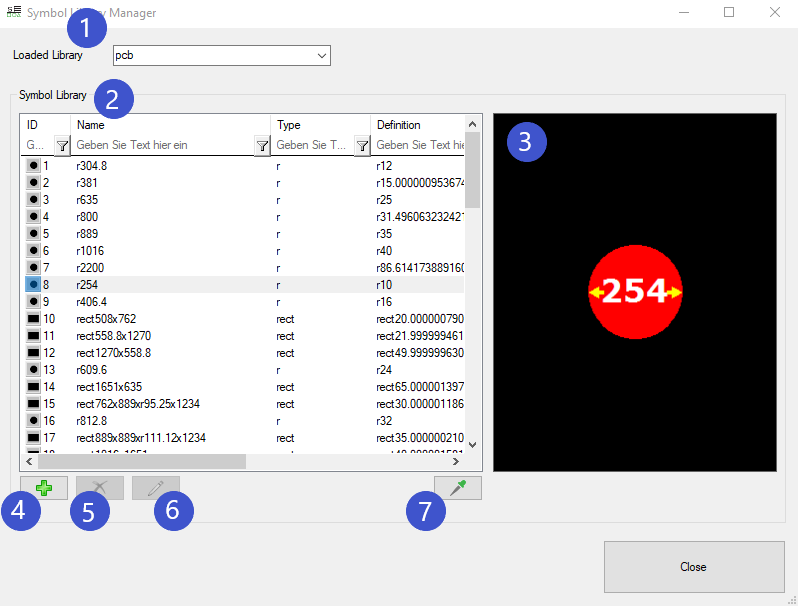
1. Under “Loaded Library”, you have three different types of libraries to choose from:
To get access to the symbols of one of these symbols, you have to open the subcategories of the corresponding library.
2. Then, you will see a list with all symbols and their properties stored in this library.
3. Selecting one of these symbols in the list, will visualize them on the right side of the list.
4. Clicking on the green plus at the bottom left corner of the dialog will open the following dialog:
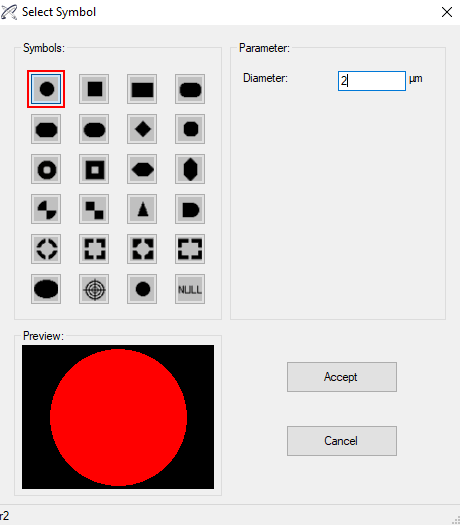
Here, you have the choice between different ODB++ symbols that can be adjusted according to your needs by defining their parameters. Clicking on “Accept” will then add the newly defined symbol to the currently opened Library.
5. Clicking the “X” when you have selected a list item, allows you to extinguish this symbol in your library.
6. Clicking on the pen symbol will open up the “Symbol Property Editor”.
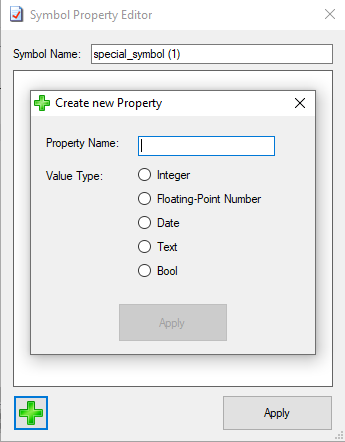
The Symbol Property Editor allows you to change the name of the symbol and create a new property by entering a new property name and by choosing a new value type for the symbol.
You can´t delete or edit the properties of a symbol that is a regular feature of your design. When you have selected one of these symbols, the two buttons will be greyed out.
7. If you have selected the currently opened Job as a Library, you have the option to pick any of the symbols on your design in the graphic interface and the corresponding symbol in the list will be highlighted.
There are two more options when you have selected an XML or 365 Library to work with. The dialog for these libraries will also look a bit different:
When choosing either an XML or PCB-I 365 library, you can click on ![]() to open another dialog for adjusting the settings of the library.
to open another dialog for adjusting the settings of the library.
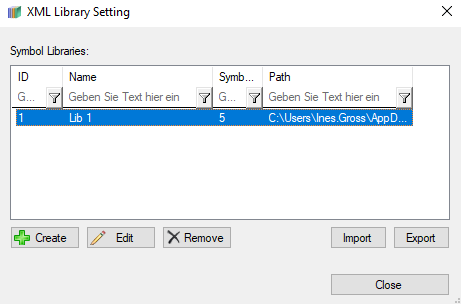
This editor allows you to create, edit, remove, import and export a (new) library. When adding a new library (click on “Create”), you have to enter a new name for the library and you have to select the propriate path for the library file you want to choose.
If you want to remove a symbol library in the setting dialog by selecting it and clicking on “Remove”.
You can also edit the parameters of an already existing object or add a new symbol from the current selection. Clicking on ![]() or double-clicking on a symbol in the list will open a new window of PCB-Investigator allowing you to adjust the currently selected symbol in the list to gain a special symbol that’s not contained in any of the libraries.
or double-clicking on a symbol in the list will open a new window of PCB-Investigator allowing you to adjust the currently selected symbol in the list to gain a special symbol that’s not contained in any of the libraries.
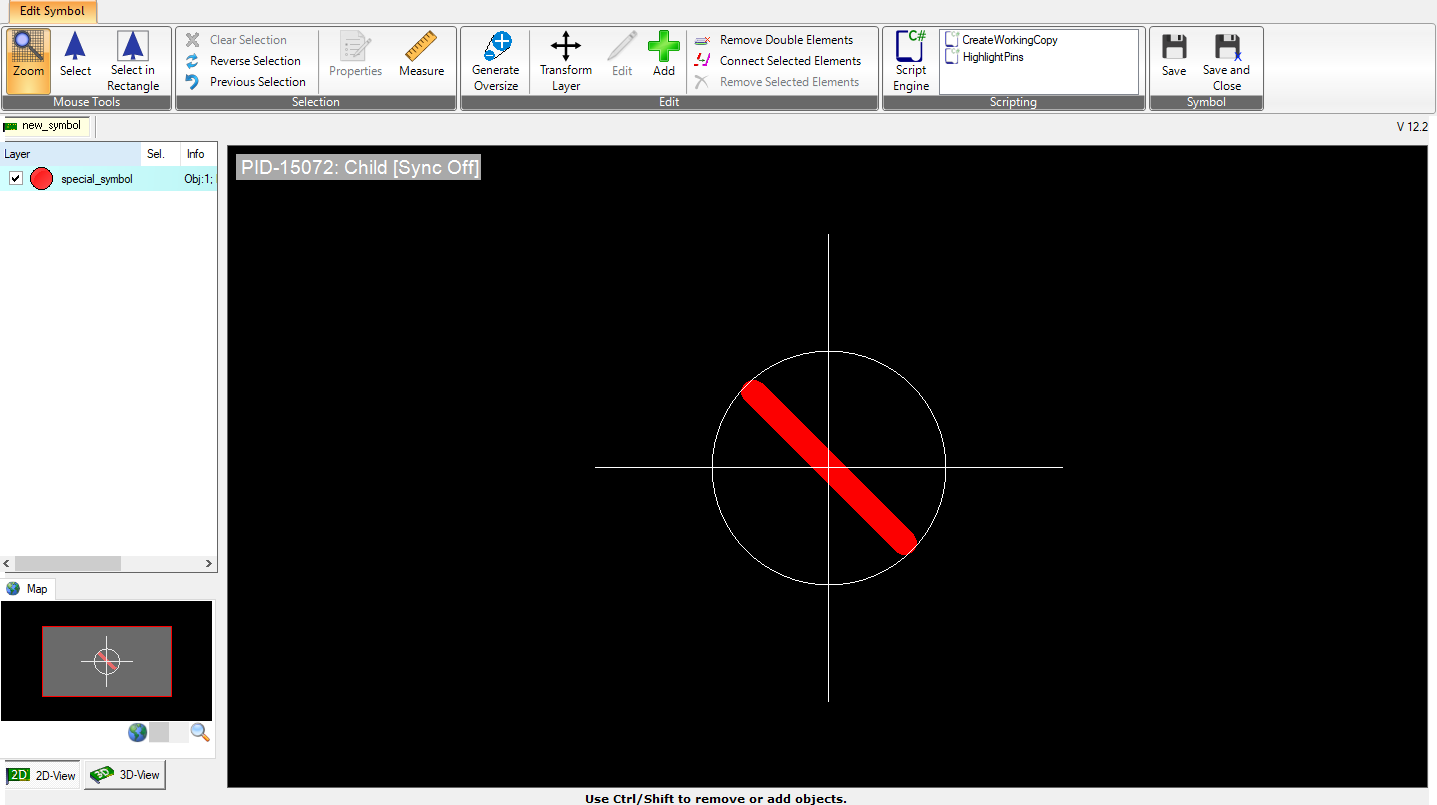
To configure this symbol, you can then click on “Add”. This allows you to compile a special symbol. How to add symbols or objects is described under “Add Objects”. If you have completed the compilation of your special symbol, you can click on “Save” or “Save and Close” on the upper right corner of the window and you will get back to the main Symbol Library dialog.
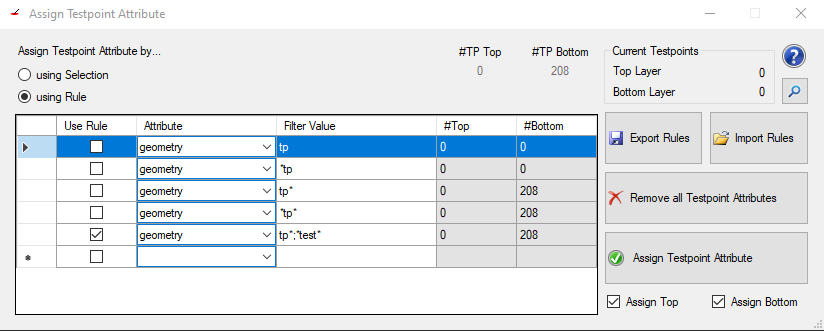
You can find the Testpoint Assign Tool under Plugin >> Assign Testpoint Attribute.
This tool helps to find and mark testpoints in a layout which could be defined via multiple non standardized attributes. Marking them with this tool then helps to standardize this and prepare the layout for following tools (for example the DFT Preperation).
On the top left you can switch between using the current selection or a set rule to find the testpoints and assign the test_point value.
When choosing rules you can add another rule by checking the checkbox of the lowest row in the current listview and then fill out which attribute should be tested and what value needs to be set in said attribute.
All attributes are listed in a simple drop down menu. The Filter Value then has to represent the value of the attribute. Wildcards are allowed when searching for attribute values. The image shows for example all ways to search for "tp" in the "geometry" attribute:
Also it is possible to search for multiple values of the same attribute as shown in the last row. Simply seperate the values with a semicolon.
Boolean attributes do not need any value since their existance already means they are set.
To remove a rule simply select the whole row by clicking on the left most column of the row you want to delete (left of Use Rule) and press the "delete" key on your keyboard.
Checking a rule will select all found possible testpoints of the job (the checkboxes Assign Top and Assign Bottom change the selection depending on the check state of them)
On the top right side there is an information panel showing:
Export Rules exports the currently set rules to a xml file on selected location on the machine or in a cloud
Import Rules imports rules from a file either from the machine or from a cloud
Remove all Testpoint Attributes removes the "test_point" attribute from all pads of the job
Assign Testpoint Attribute adds the "test_point" attribute to either the currently selected pads or the pads found by the selected rule (handled by the radiobuttons "using Selction" and "using Rule")
Assign Top is a checkbox that when unchecked the "test_point" attribute will not be set for the pads on the top layer
Assign Bottom is a checkbox that when unchecked the "test_point" attribute will not be set for the pads on the bottom layer
To find possible testpoints the attribute histogram is a good way to start.
The Package Group Manager is a Developer tool for setting or change your package types.
The following picture shows a few of informations(red box), where you can search or select the name of your Component e.g Package(red circle).
Important Options are shown in the following picture.
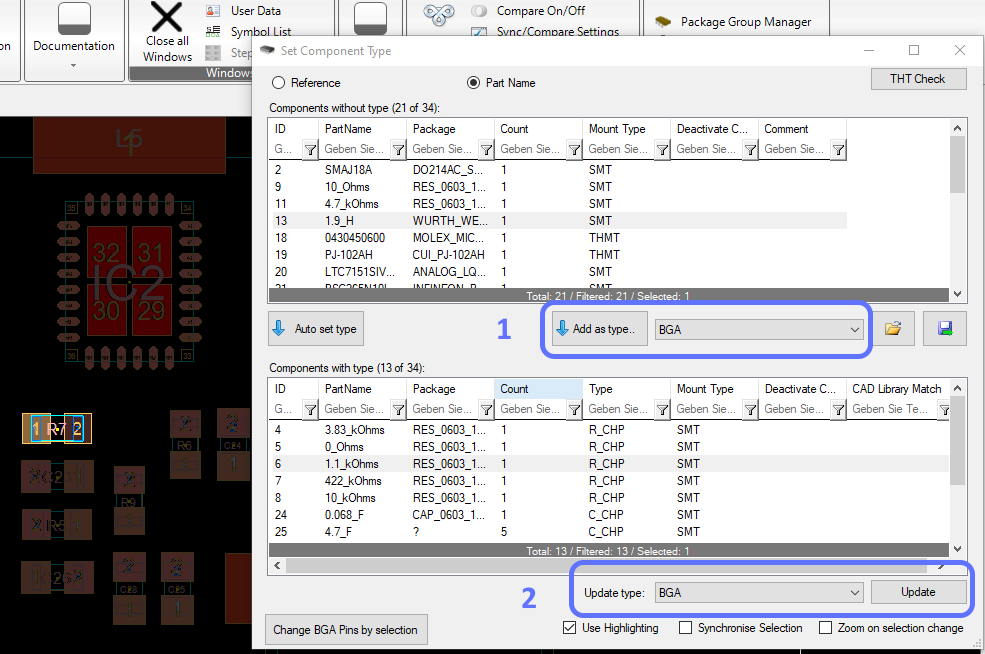
1. Add as Type added the component you selected as the type you selected in the menu next to this column.
2. Change Type allows you to change the Type of your Component. You can find the selection "Update type" in the right corner of your window.
Whether you want to change a C_CHP into an R_CHP or the other way around, you only have to click on the Update button.
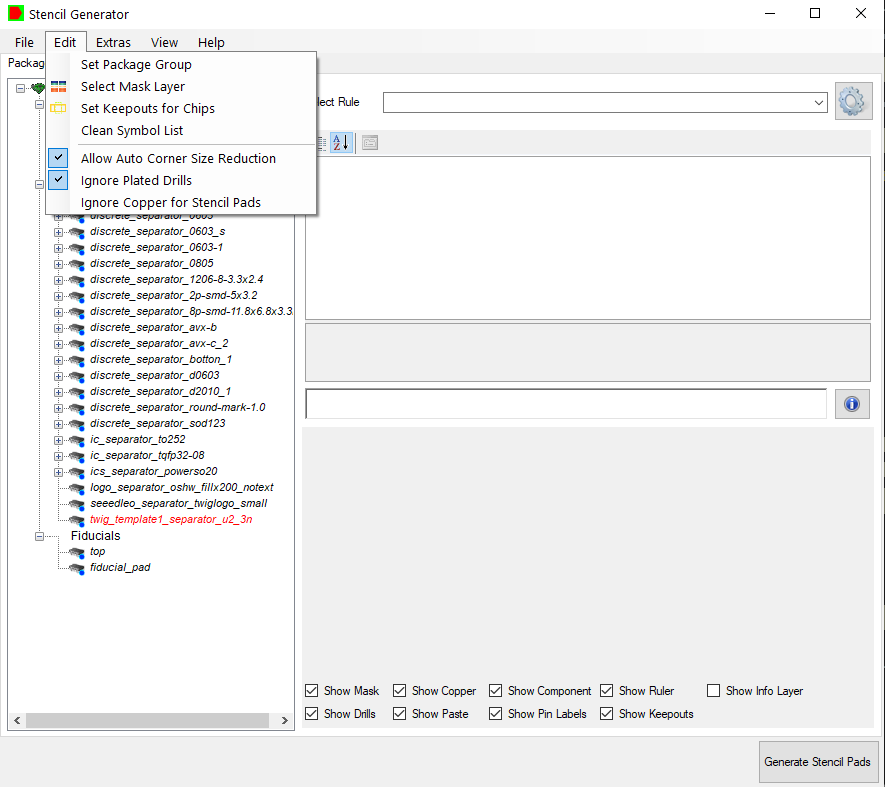
The Stencil Generator uses all zones defined by the Stencil Area Editor. If there are no zones the outline will be used as main zone. Use default rules for your company. Setting a package group, enables the Wizard to set the rules regarding it. SOICs, Chips, BGAs and any definition needed. The Wizard is delivered with predefined settings. To adjust all data preparation to your product you can setup own data preparation Scripts to adjust to your equipment.
Set Package Group is only necessary if your data don’t contain a proper information. Customers with EPL (“Easylogix Part Library”) can resolve trusted data from EPL. The Wizard also process layouts with multiple mask layers in the stack-up. Set “Keepouts for Chips” is only available if you have MPN packaged defined. It will handle the usable area for you. You also can set plugged drills as free usable area.
You have the possibility to set rules by package, set extra rules for components in defines zones or to set a rule for each component.
To set another rule to your component, select one in the given list.
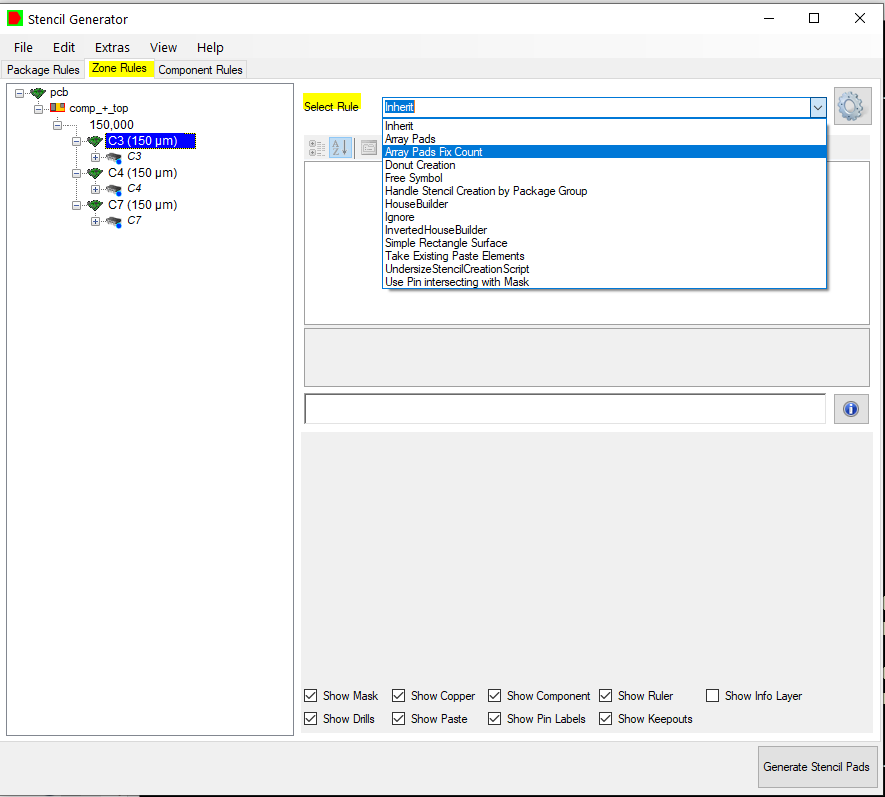
You can add your own rules by clicking on the setting symbol.
Send the stencil data in your preferred format to your supplier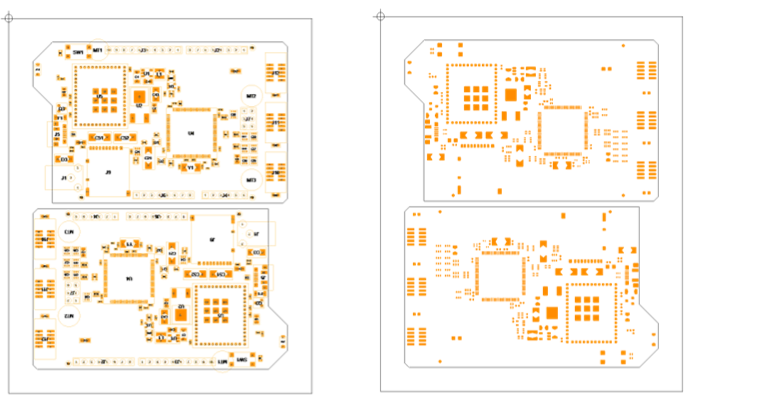 |
Result of the rule-base stencil wizard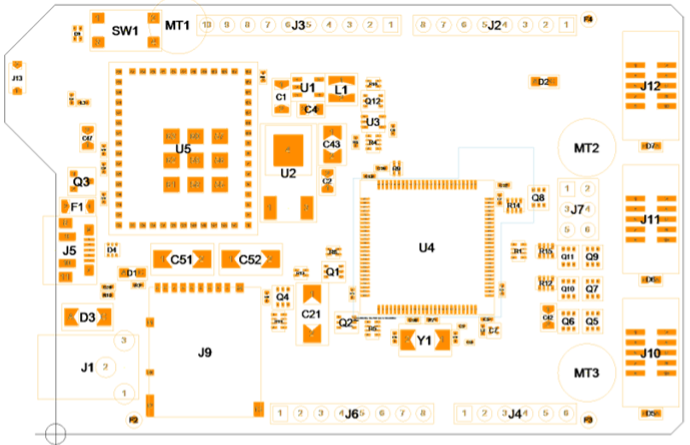 |
Before and after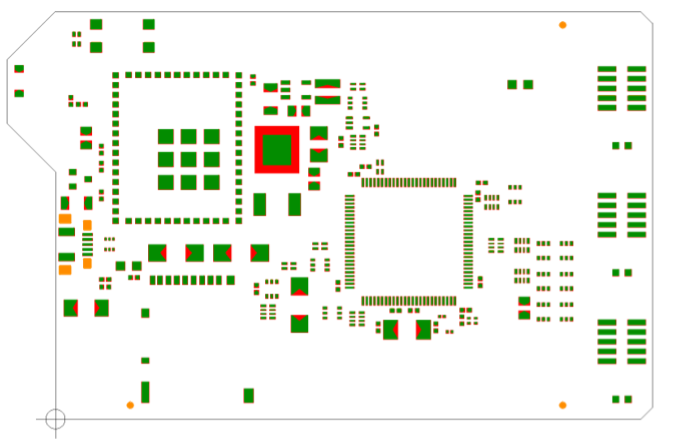 |
Stencil pad details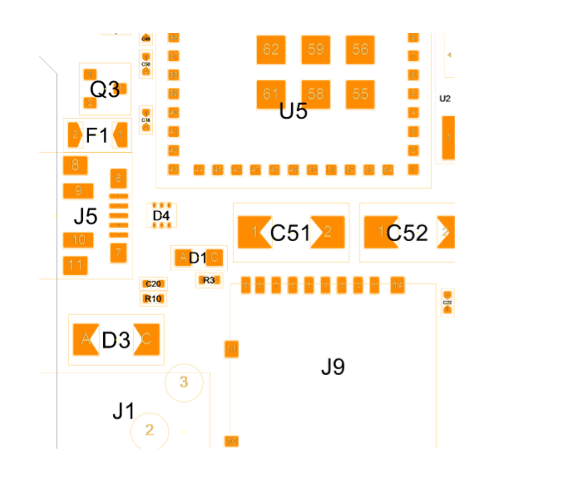 |
Here is a short video to show special cases in one of our demo designs:
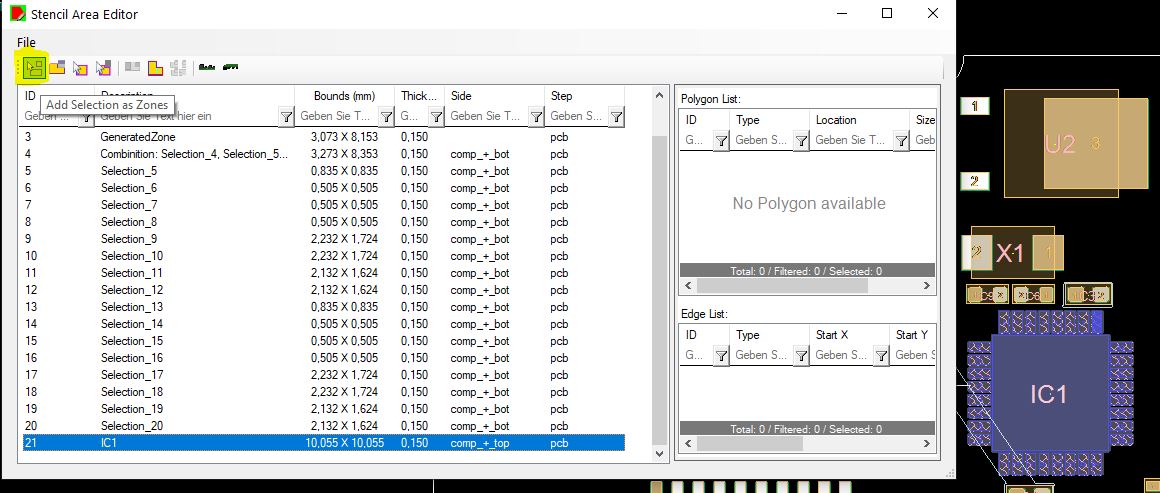
Note: For high quality, it is recommended not to cut pin pads. You can combine areas e.g. from different parts to get ideal areas.
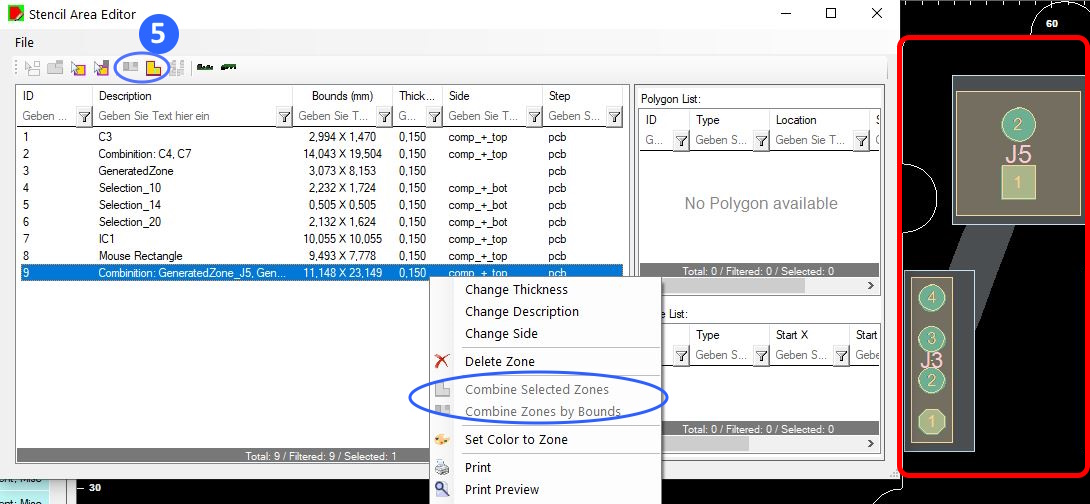 Combine different zones to one zone
Combine different zones to one zone
-->Zone settings can be saved in ODB attributes, exported as xml and imported from xml.
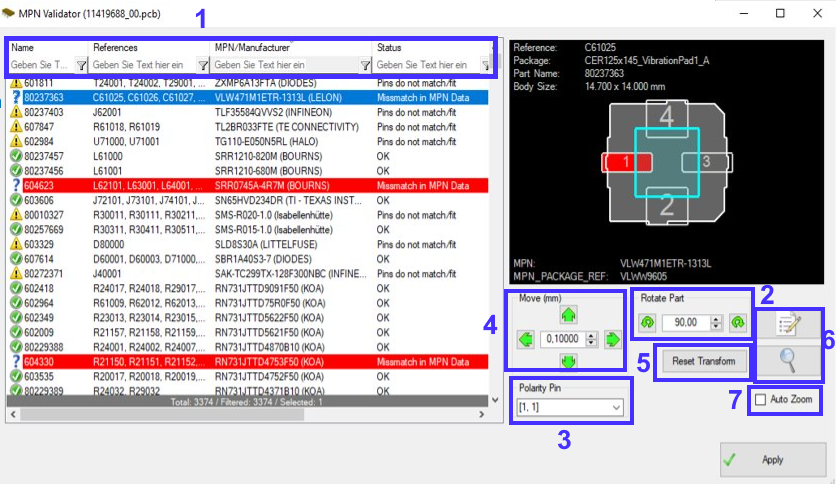
Check-In/Out of the design (you can block changes for other users by checking out the design) and Freeze a design if it should be blocked for all changes
Panel Builder brings an template manager with it, there are options to store panel templates and an coupon library online or local.
With the templates you can use standard panel sizes with fix drill and marker positions. It is possible to store templates for each layer count, depending to the size of the useable area it calculate the amount of single PCBs in the template.
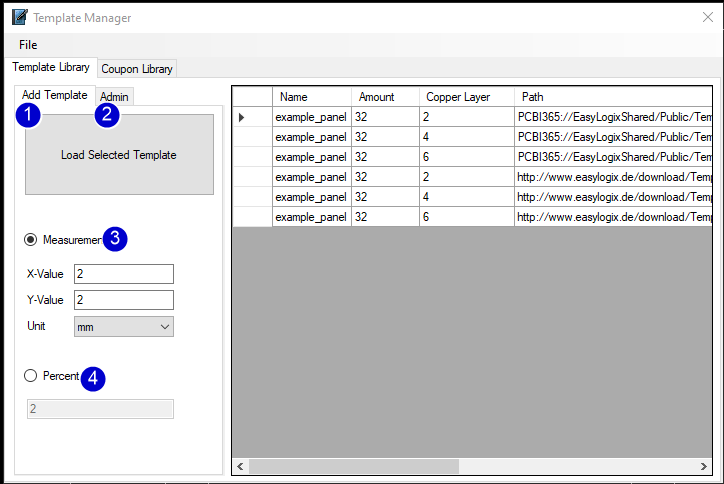
1) Add Template from the list on the right side
2) Change to Admin area
3) Options for distance in fix values
4) Option to fit single pcb with percent distances
Admin Area

1) Add the current design as template to the list.
2) Remove the selected template from the list.
3) Open the update dialog with many more options (useable ares, copper layer count, path to the template and step name)
Coupon Library
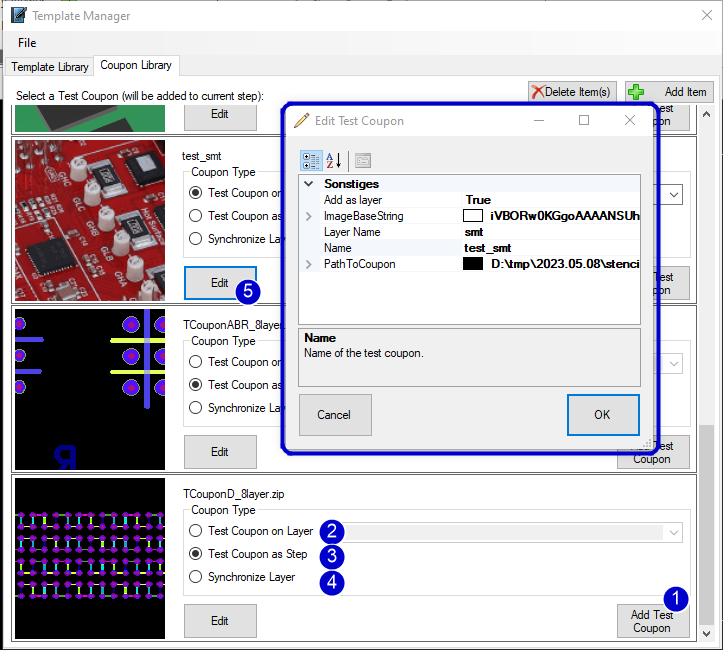
1) Add the selected coupon to the panel.
2) select "Test Coupon on Layer" to add the loaded coupon entry on one layer.
3) select "Test Coupon ad Step" to create an new step with all coupon information (recommended for coupons with components and net information)
4) select "Synchronize Layer" to fit the coupon data on the panel layers.
5) Edit the coupon entry, e.g. change image or path to the coupon.
If you want to add new symbols or logos you can handle this symbols in an own library, here is a short video how to add an dmc place holder on the panel edge:
This is only a simple example how to use existing symbol library for and DMC spaceholder Pad. We provide some libraries, but it is also easy to copy existing elements in our managed libraries to store connections directly in PCB-Investigator.
The Production Tool Editor to define solder frames:

The solder frame definition based on an single PCB with fixing elements as well as down holder with routings for spcial cases like THT components.
The Production Tool Editor to define coating carrier:

The coating carrier base on an standard frame (or special format) with down holder, fixing elements and many more. You can individually change the coating machines to create coating areas and check the frame use legal regions for coating. For better support in the frame you have options to use different routings and depending on the extra material it automatically creates the openings for the coating machine heads.
The Production Tool Editor to define workpiece carrier:

Workpiece carrier containing extra elements and routings, this simple frame create an simple transporting frame with down holders to fix the PCB in the production process.
The Production Tool Editor to define supporting plates:

Supporting plates for pressfit actions in your production line do create routings and documentations for the export files.
The Production Tool Editor to define adapter definitions:

The adapter definition is the most complexe production tool, it contains all standard cases for special testing routines e.g. high voltage checks or vacuum systems. Special handling for connectors, LED Checks, switches or press buttons included.
You can handle stops and fixing elements as well as routings for high components and down holder or supporting stamps. After defining all important elements it is possible to add an example adapter panel to export the adapter package for one DFT Session.
The export contains additional files to create 3D modells like this:

(3D view contains PCB, models for fixing pins, extra electronic and the adapter case)
1. Line

1. At first, you have to choose the layer on which you want to add a line.
2. If you want to add attributes to the line, you have to set a hook next to “attributes” and then click on values. Another window will open, which allows you to choose the propriate attributes.

After you have chosen the propriate attribute, click on “Add or Overwrite”. To add the selected attributes, click on “Accept”.
3. You can also decide, whether you want to add a positive or negative line (polarity). If you would put a negative line above a positive on, the negative line would cut away the overlapping parts of the lines.
4. To select the type of line you want to add, you have to click on “Symbol” or you have the option to pick a line that’s on the currently opened design. Clicking on “Symbol” will open up another dialog, the Symbol Library. You can then select the propriate line from the symbols provided there. For more information on how to work with the Symbol Library, move to “Symbol Library”.
How to add a line: After the selection of the symbol type, you can now add the line. To do so, right-click on the position in your design that you chose for the new line. A double-click will end the line.
5. You also have three more different options when it comes to adding lines:
6. You are also able to place lines by entering the X and Y coordinates of the start and end point. “Add” will then place the line.
7. The yellow button allows you to check for shorts while creating new lines (depending on net option), the white button colapse the dialog while routing.
2. Pad
If you want to add pads, click on the button "Pad". You will then see the following window.

The adding of pads works analogous to the adding lines.
There are only a few different options that have to be additionally explained.
You can choose whether to mirror the pads to be placed by setting a hook on either Mirror “Yes” or “No”.
Another option is the configuration of the angle (0°, 90°, 180°, 270°) that shall be used when placing the pad.
3. Surface
If you want to add a surface, click on the button "Surface". You will then see the following window.

When adding surfaces, there are also a few options differing from the addition of lines. These shall also be explained here.
If you want to add a surface, you have three options:
Polygon
You can either place a polygon by entering the X and Y coordinates. Enter the coordinates and click “Start”. The defined point will be the starting point of your polygon. Enter new coordinates and click “Add Point”. You can then continue with this procedure until you want to close your polygon. To do so, click “close”.
The other option for placing polygons is just to do a simple right-click at the propriate position in the design. Continue to place more angles of the polygon by further right-clicks. A double-click will automatically close the polygon.
If you place an angle in a way that will hinder the automatic closure, the new (wrong) line will be shown as red instead of blue.
Besides the polarity, you can also select whether to place an isle or a hole into an existing surface. It`s not possible that holes cut each other.
Rectangle
To add a rectangle, you can either also use the method of entering X and Y coordinates or you can select the starting point of your rectangle by a simple right-click. The size of the rectangle can then be determined by moving the mouse. Double-clicking will place the rectangle.
Like when defining the polygon, you have the same two options: You can also select the polarity and whether to place an isle or a hole into an existing surface.
Flood Layer

To flood a layer, you have to adjust some parameters to configure the distances that shall be held and the minimal area (regarding the min. total area) and size of the flooding (regarding the min. length /width):
In the case of “Flood Layer”, the use of entering X and Y coordinates is not reasonable.
4. Arc
If you want to add an arc, click on the button "Arc". You will then see the following window.

When adding arcs, there are also a few new options that haven´t been explained yet.
Firstly, you have to define the diameter. You can either define it by entering a specific value or you use the pick tool (“Pick Diameter”) to choose a propriate diameter that has already been used in the graphic interface.
When placing the arc, there are three different methods for setting it:
You can also decide for the direction when placing the arc. You can either choose to place it clockwise or counter clockwise.
5. Text
If you want to add a text, switch to the button "Text". You will then see the following window.

To place a text, you can decide for the polarity (positive, negative), if you want to mirror the text (mirror, no mirror) and the angle of placement (0°, 90°, 180°, 270°).
You can either place the text by entering values for the X and Y location or you can place it by double-clicking on the propriate position on your design in the graphic interface.
The “X-Size” and “Y-Size” refer to the width and length of the letters.
A simple right-click adds the text on your design in the graphic interfact. You can still place the text on another position by simply moving your mouse. A double-click will then place the text.
You can configure the view that you see on the right (2) by selecting the wanted attributes and properties on the left side (1).
The Left Side is called the Property List while the right side is called the Component List
The properties selected on the left side will then show up on the right side. The order of the columns is determined by the order in which you have selected the properties in the listview on the right. If you want to change the order you can also drag and drop the different columns to the position you want. Important to note is that columns like id, reference and the SumUp Column will be moved back to the front after you reopen the Component Manager. Sum Up will add the different rows together and aggregate the rows based on the selected values.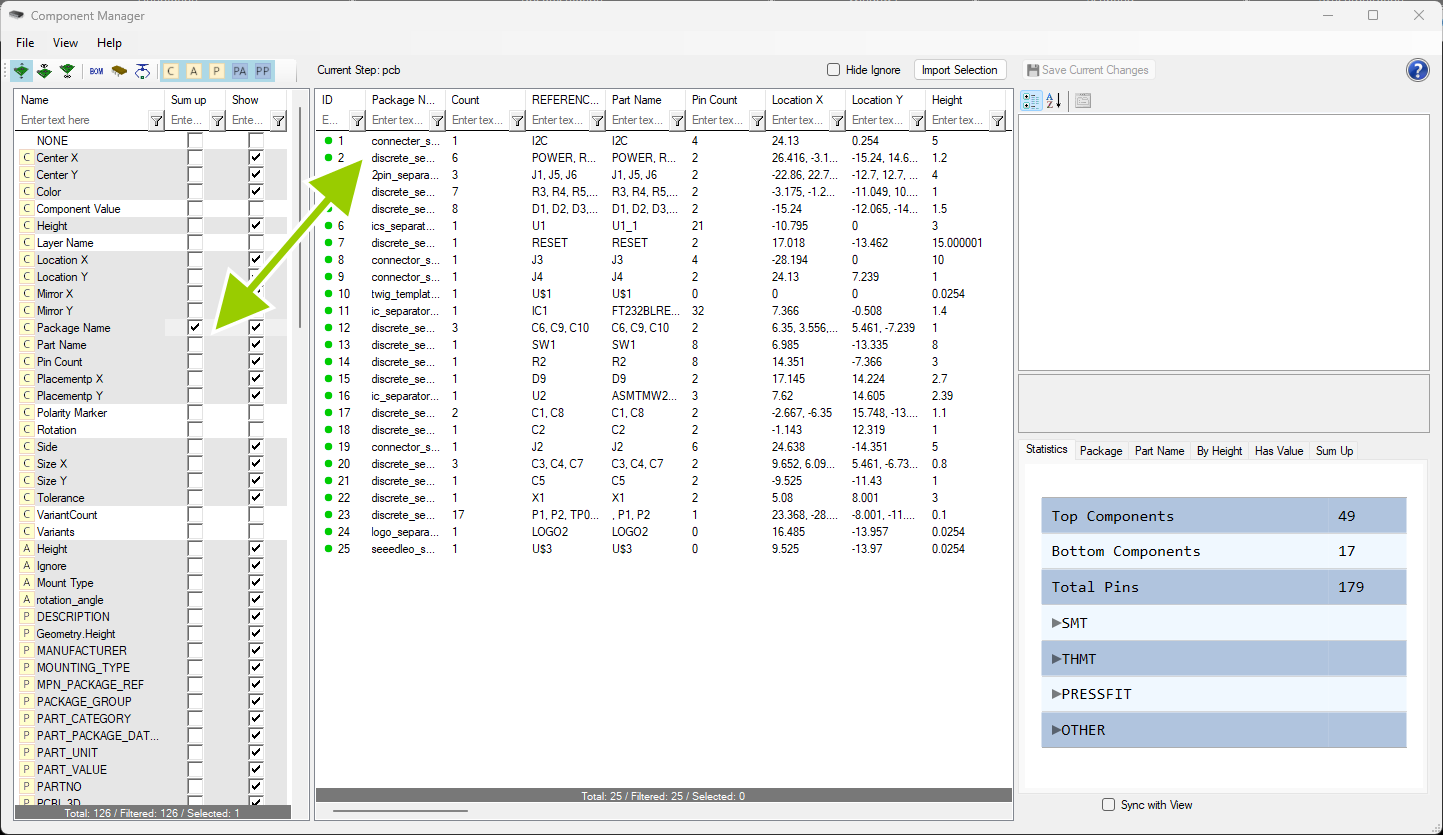
The different icons inside of the Property List define what kind of attribute it is, while the dot besides the component in the Component List shows the change status of the component. The legend for the different icons is as follows.

You can select multiple different settings to adjust the view quickly.
![]()
From left to right they to the following.
By right clicking the component list you can export the current view to and Excel or HTML file.

Items selected inside of the Component List can be edited inside of the property grid on the right side.

Any changes to the component will lead to the green dot turning orange. You can save the changes by either clicking the button above the property grid and saving or pressing the save option in "File" in the top row. Until then there are no changes that are actually saved and applied to the real components. If you select multiple components at the same time, or use the Sum Up which leads to a row representing more than one component, the property grid will show you only the values that are the same between all components. Any changes inside of the property grid will then edit all objects at the same time. Properties shown are not necessarly present in all components selected. If one component has the property then the property will be shown. If a value is then edited, the components that do not have the property will be given the property.
The Cutout Editor helps you to create additional elmenets and modify the cutouts:

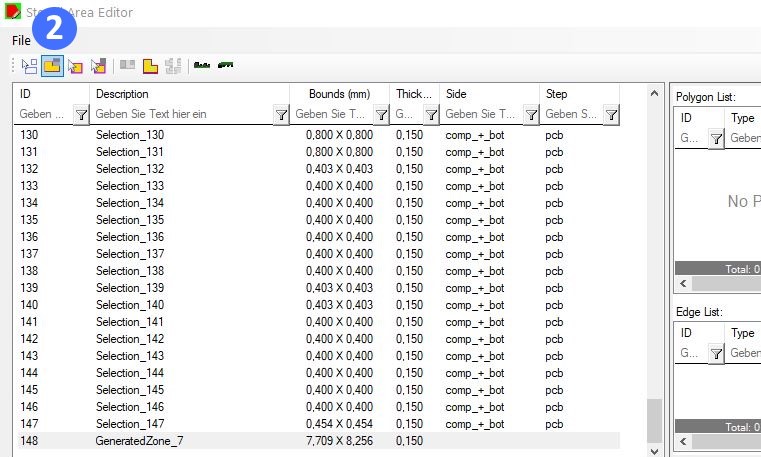
1) List of all cutouts, they have an running ID and a Location X/Y for special cutouts there is also and End X/Y and an repeat Index (for each child step).
2) Edit area for the cutouts, you can modify the Location.
3) Additional Element Area, here you can define what you need on different layers
4) Auxilary Drills is special, you can generate mousebites for one or both sides.
For setting mouse bite drills we have a second video:
The Package Library Manager handle all libraries for packages, this could be e.g. an 365 library, an lite DB or an xml library and customized libraries:

You can edit the packages here and change properties.
Here is a short video to show how you can add your own library:
The part library manager gives you options to edit your list of part libraries:

With some options to copy/delete/add new parts you can manage your libraries here and manage the available libraries in the settings dialog:

The library types containing data from the open Job/Design, local types like xml or lite DB and online types like API Part Libraries, REST Libraries and out 365 Libraries:

With the context menu you have options to copy or edit the part, you can export the library list and search for specific information:

Here is an short video how to bring parts in your library:
use the pencil button to edit package properties in an seperate dialog:

Depending on the library type there are different properties available, with 365 libraries you can manage your properties in admin area or in xml library you can directly change the available properties.
use the pencil button to edit part properties in an seperate dialog:

Depending on the library type there are different properties available, with 365 libraries you can manage your properties in admin area or in xml library you can directly change the available properties.
You can modify the package outline in an complexe editor or in the simple package editor with some basic handlings:

Here is an top area with width and height for the package outline, you have an helpfull search button and can rount/cuts the corner for the package definition.
Below you find an list with all pin definitions, each has an Geometry type like rectangle, circle or polygon with the size and the pin position X/Y.
On the right side there is an preview with simple transform options (move pin or body).
And some buttons e.g. for rotate, add/remove pins and "Make IPC Conform" to switch the definition in an library standard orientation.
Note: Our libraries have to be IPC Conform, it is only possible to save package changes if the result is IPC Conform!

In the context menu it is possible to switch pin order (Move Up/Down)
Edit multy selection, renumber the pins and change outline and pitch values.
In the graphics area you can measure, zoom switch mouse tools and change view:

Here is an short video to show some functions:
The Part Library Outline Editor is similar to the Package Editor, you have also all edit options from there:

For more information check this page here
All Nets can have net attributes, if you set an Net Group it will be handled in some plugins together.
To find out how you can set this net groups read this page

There are some basic settings to match the packages.
Pin Positions are always used, but you can change the Height information of your CAD Data to tolerance value based on the component height or ignore it complete.
Overwrite package and step information defaul by "Ask", this mean there comes a dialog with checkboxes.
How to use the Package Expert firt time?
Here is a short video how to ask Library for all components and set 3D settings:
Connect Library information with your AVL File, with individual importer it can read csv, excel and other files.
Check all components with vidual fitting helper and maybe transform wrong locations or rotations with the simple user interface:

Depending on the MPN and Manufacturer the BOM Expert search for library information and connect them with the open design, this can include properties and step files. You can automatically set no_pop/comp_ignore attributes and use custom actions with an post script to do special actions depending on the imported data.
The Settings containing a list of importers, Searchend Properties and settings to handle not found components. It also has options to add missing entries in an intermediate library and an post script (found by GUID in your favorites).

Unknown => It is not possible to give more details
ReferenceNotInDesign => The reference in imported data is not available in the design
ReferenceNotInAVL => The component in the design has no entry in imported file
NoPartAvailable => The part list do not contain results in the selected library
NoPartSelected => No part selected mean the user has to select one
NotFoundInLib => The library do not contain a fitting item
SelectedPartDoesNotMatch => There is a maybe wrong part selected, please check the selected part
OK => Part is OK
OKUnverified => The pin matiching is not checked but the part is marked as OK
To automate your custom stencil scripts, it is necessary to use the StencilCreationScript interface.
Here is a link to see all details for your implemention manual.
You have to set public porperties to give user options to change in the property grid, there is also a method to create the preview and the pads. You should fill the corde with all calculation you need e.g.
public bool CreatePads(IPCBIWindow parent, IStep step, IODBLayer StencilLayerOutput, InterfaceCMPObject BasicObjects, List<IPolyClass> UsedPinPads, List<IPolyClass> MaskForCheck, List<IPolyClass> Drills, double ThicknessPaste)
{
if (StencilLayerOutput == null || BasicObjects == null || UsedPinPads.Count == 0)
return false;
bool IntersectWithMask = false;
CreateRectangleElement(StencilLayerOutput, UsedPinPads, MaskForCheck, Drills, BasicObjects, out IntersectWithMask);
return true;
}

In the options area (1) you can add your custom developed scripts (2).
Main Interface

This tab manages soldering rules for components and packages:


Sessions, settings, and results can be imported and exported individually for easy sharing and reuse.
In stencil design, a donut shape is used to define a circular opening with a central void (hole), commonly used for thermal reliefs or annular ring designs. The donut is generated around a pad center based on several configurable parameters.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
InnerDiameter |
double | Defines the inner diameter of the donut. This is the size of the central hole that will not be cut into the stencil. |
OuterDiameter |
double | Specifies the outer diameter of the donut, representing the total size of the stencil opening. |
AngleStep |
double | Angle between each arc segment when constructing the donut shape. A smaller step creates a smoother circle. |
OffsetX |
double | Offset in X-direction from the pad center, applied to reposition the donut shape. |
OffsetY |
double | Offset in Y-direction from the pad center. |
Rotation |
double | Applies a rotation (in degrees) to the donut shape around the pad center. |
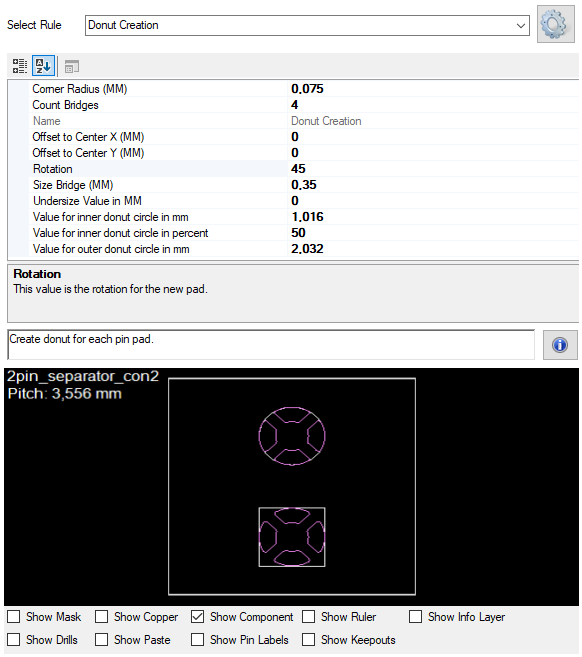
These properties are used by the StencilScriptDonut class to calculate and render the donut shape on stencil pads. The donut is typically composed of an outer arc (outer diameter) and an inner arc (inner diameter), combined with connecting lines to form a closed shape.
Ensure that InnerDiameter is less than OuterDiameter to create a valid donut. Adjust AngleStep based on performance vs. accuracy needs.
Array creation is used to replicate pad openings in a structured pattern. This is especially useful for components like QFP or QFNs,
where cooling pads are very big and replaced by array formation. The array is defined using specific rules and transformation parameters, it gives you an easy way to define an array of similar (rounded) rectangles.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Array Field Count in X direction |
int | Fix Array Rule only: Array pads count in X direction. |
Array Field Count in Y direction |
int | Fix Array Rule only: Array pads count in Y direction. |
Corner Radius (MM) |
double | Corner radius for rounded elements in MM. |
Utilization Array Area (%) |
double | Utilization of avalable area in percent (only used if no fix size is used and value >0). This option will ignore the undersize value and depending to the settings it is possible the values are not exact. |
Minimum Array Field Size (MM) |
double | Array pads has minimum this size, if there is only space for one pad no array created. |
Offset to Center in X direction (MM) |
double | Fix Array Rule only: X offset to shift the array from the pad center. |
Offset to Center in Y direction (MM) |
double | Fix Array Rule only: Move array in Y direction from center of the pin. |
Distance Array Fields (MM) |
double | Array pads has this distance to next pads. |
Undersize Value in MM |
double | This value is only used if no Array size is defined. All other Elements will use this value in mm to generate undersize. |
Ignore Mask Intersecting |
bool | Do not check for mask intersecting (add all array elements without checking mask). |
Array Size Width (MM) |
double | Width for complete array, if it is =0 the original element width is used. |
Array Size Height (MM) |
double | Height for complete array, if it is =0 the original element height is used. |

These properties are used in the StencilScriptArray class to define how shapes are duplicated and transformed. Each array pattern follows a specific logic:
- check avalable size of array
- check max pad size and gap value
- split area in pads and round the rectangles
Use array rules to easily build consistent and scalable designs for components with repeated pad layouts.
Adjust offset values to fine-tune placement, it also has an utilization property to gives the rule an optimum of area.
The StencilScriptHouse class defines the necessary parameters to create a house structure around a stencil pad for solder paste applications. It is used for automating stencil generation and includes geometry, shape characteristics, and spacing considerations.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Corner Radius (MM) |
double | Corner radius for rounded elements in MM. |
Offset to Center (MM) |
double | Move houses to the center of the component. |
Invert Direction |
bool | For smaller elments sometimes the house should be show away from the component. |
Undersize Value (MM) |
double | All Elements will use this value in mm to generate undersize. |
House distance cut size in Percent |
double | Value in percent depending to the height of the pad. |
Utilization House Area (%) |
double | Utilization of avalable area in percent. This option will modify the cut size value to come near to the percent value. Use 0 to ignore this value. |
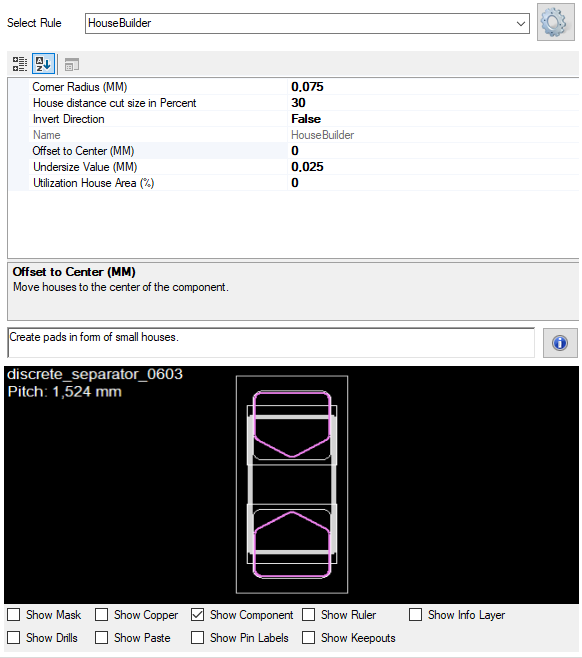
These parameters help define the geometric and contextual constraints for automatically generating stencil pad protection using a house-shaped perimeter. The house rule is recommended for chip packages, but can be used for all pins with clear directions.
Note: If the pin is under the body the direction cannot be calculated and no house is created.
Depending to the chip size it is recommended to change from house to inverted house rules.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Corner Radius (MM) |
double | Rounding on the corners. |
House distance cut size in Percent |
int | Value in percent depending to the height of the pad. |
Invert Direction |
bool | For smaller elements sometimes the house fhould be show away from the component. |
Max Size of one Element (MM) |
double | Each element has maximum width and height, if the size is bigger it is automatically splitted in more elements. The value is in MM! |
Undersize Value (MM) |
double | All elements will use this value in mm to generate undersize pads. |
Offset to Center (MM) |
double | Move houses to the center of the component. |
Step for Big Elements (MM) |
double | If the element is bigger Max Element Size it use this value to split the size in more elements. |

These properties are used in the StencilScriptInvertedHouse class to define how shapes (such as stencil pads or vias) are duplicated and transformed. In general this rule is used for Chip Packages.
Note: If the pin is under the body the direction cannot be calculated and no house is created.
The StencilScriptSimpleSurface class defines the necessary parameters to create a rectangle structure around a stencil pad for solder paste applications. It is used for automating stencil generation and includes helpfull options.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Corner Radius (MM) |
double | Corner radius for rounded elements in MM. |
Try Find Direction |
bool | Rotate surfaces depending to the direction of the pin. |
Rotate Bridges 45 Degrees |
bool | All bridges are rotated 45 degrees to obtain diagonal openings. |
Offset to Center X (MM) |
double | Move rectangle in X direction from the center of the pin. Or if you use negative values away from center. |
Offset to Center Y (MM) |
double | Move rectangle in Y direction from the center of the pin. Or if you use negative values away from center. |
Bridge Width (MM) |
double | Use bridges to cut the rectangle with this width. |
Bridge Count X |
int | Use bridges to cut the rectangle with count in X direction. |
Bridge Count Y |
int | Use bridges to cut the rectangle with count in Y direction. |
Offset move away disctance (MM) |
double | Move surface away from center point, this is only for outer pins (not for cooling pins). |
Size Width in MM |
double | Width for this pad. |
Size Height in MM |
double | Height for this pad. |

These parameters help define the geometric and contextual constraints for automatically generating stencil pad protection using a rectangle-based-shaped perimeter.
Note: The simple rectangle rule ignore the mask opening and overprint it!
The StencilScriptUndersize class defines the necessary parameters to create a similar structure around a stencil pad for solder paste applications with smaller size. It is used for automating stencil generation and includes geometry, shape characteristics, and spacing considerations.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Undersize Value in Percent |
double | All Elements will use this percent value on the smaller side to generate undersize. |
Undersize Value in MM |
double | All Elements will use this value in mm to generate undersize. |
Corner Radius (MM) |
double | Corner radius for rounded elements in MM. The value is independent of the undersize and can change the earthings with different values. |
Max Size of one Element (MM) |
double | Each element has maximum width and height, if the size is bigger it is automatically splitted in more elements. Value is in MM. |
Steg for Big Elements (MM) |
double | If the element is bigger MaxElementSize it use this value to split the size in more elements. Value is in MM. |
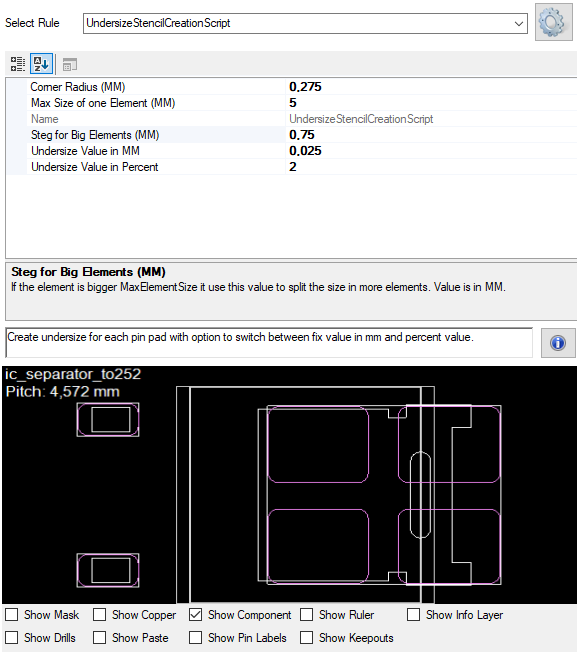
These parameters help define the geometric and contextual constraints for automatically generating stencil pad protection using a smaller-shaped perimeter.
Note: If the undersize values to small no pad will be created, the rule checks the mask layer for intersecting!
The StencilScriptUsePinMinusMask class defines the necessary parameters to create a pin bases structure. It is used for automating stencil generation and includes geometry, shape characteristics, and spacing considerations.
This rule gives you the option to use the pin outline as basis with following options:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Undersize Value in Percent |
double | All Elements will use this percent value on the smaller side to generate undersize. |
Undersize Value in MM |
double | All Elements will use this value in mm to generate undersize. |
Overwrite All Pins |
bool | Overwrite all pins regardless of the underlying pads. Set this property to false if you want to change single pins with different rules! |
Corner Radius (MM) |
double | Corner radius for rounded elements in MM. The value is independent of the undersize and can change the earthings with different values. |
Ignore Mask Layer |
bool | Take Pin without Mask Intersecting! This do not check overlappings and openings in the mask layer. |
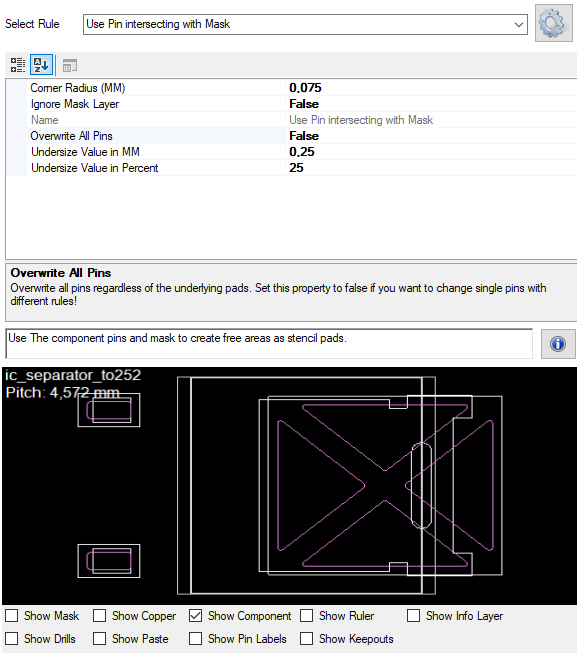
These parameters help define the geometric and contextual constraints for automatically generating stencil pad protection using the pin definition as basis.
Note: If the undersize values to small no pad will be created, the rule checks the mask layer for intersecting and it is a special handling for Overwrite All Pins to replace all pins with one rule!
In PCB-Investigator there are many options to edit or set the PCB-Outline/Profile:

1. Set by Rectangle: This allows you to draw a rectangle with your mouse cursor
2. Set Rectangle by Selection: It creates the profile around all selected objects, this is always the bounding box rectangle
3. Edit Profile: this opens an extra dialog similar to surface edit in the edit dialog
4. Set by all Objects: sets an rectangle profile around all objects
5. Get Bounds: This show a message box with the size and offset of the current step
6. Clear Outline: With this button you can clear the outline and remove all existing profile elements.
7. Add active Layer(s) to Outline: You can add the active layer to the profile, be carefull maybe you have to Clear Outline first.
8. Add Selection to Outline: By selecting important objects like drill holes or routings you can add them to the existing outline.
9. Create Layer from Outline: This create a new layer with lines and arcs on it to export or modify the profile, if you use Add active Layer(s) to Outline (7) after Clear Outline (6) you can use the modified profile
10. Set from Selection Middle: to use online the middle of your selected lines and arcs you can override the existing profile e.g. by an routing way
11. Add from Selection Middle: this is the same like 10 but do not override the existing profile, it only adds the closed way in the selection
12. Set from Selection Holes: with this option you can use only the inner area of an routing way or a hole in an surface for the profile
13. Set PCB Outline: this allows you to define the profile with many mouse clicks